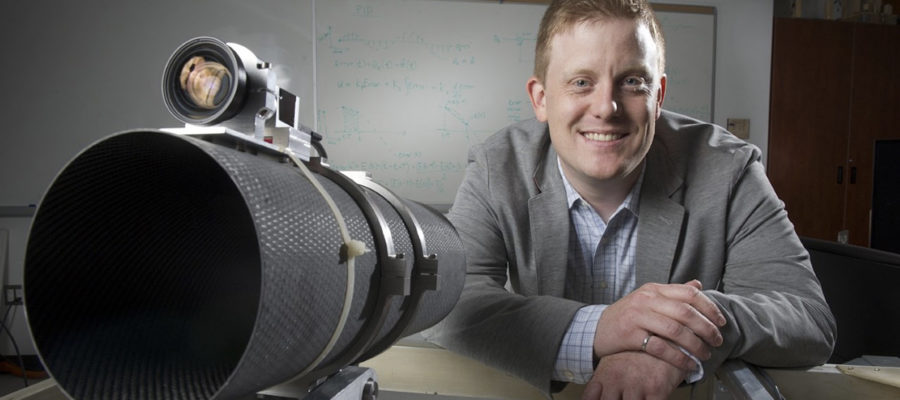
NASA liked what it saw during a series of tests of a U of G-made robotic telescope mount. The device performed better than expected aboard a converted spy plane cruising at 70,000 feet. The first-ever moonlight tracking device will improve the accuracy of numerous Earth-observing satellites. A series of test flights took place in November.
Researchers design moonlight tracking device with NASA